

Those weren’t ignored, they were addressed with the last link. Palestinians are not responsible for the Jewish exodus. Your argument is trying justify the Israeli Apartheid and Genocide by conflating Palestinians with all Arabs/Muslims and conflating all Jewish people with Israel.
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, or religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making the society ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal such as deportation or population transfer, it also includes indirect methods aimed at forced migration by coercing the victim group to flee and preventing its return, such as murder, rape, and property destruction.
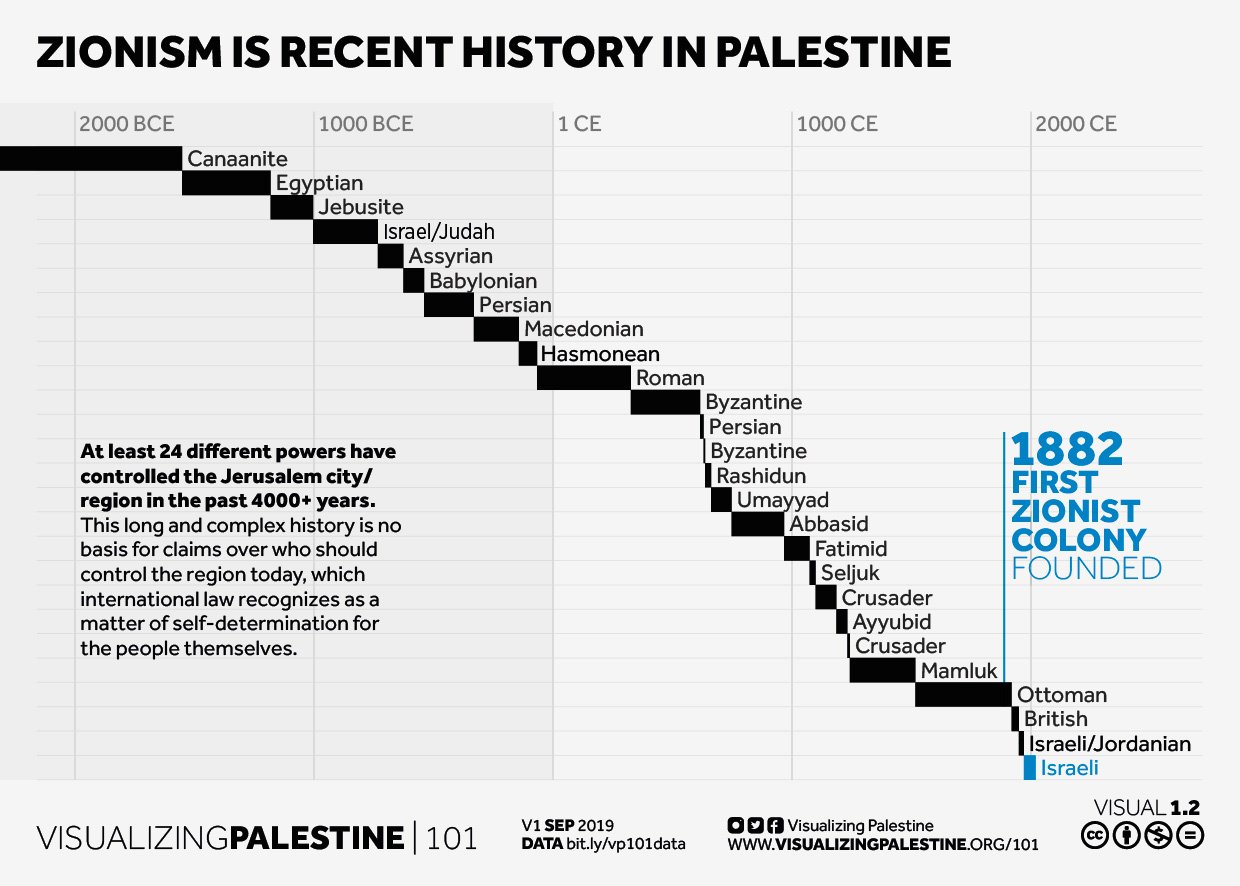
Forced expulsion of Palestinians has been central to Zionism since the 1880’s
There are a lot of factors of the Jewish exodus from the Muslim world, but your conflating of the two as justification or minimization of the Nakba doesn’t work; unless you somehow think all Arabs or Muslims are the same. But it’s pretty clear your racist towards Palestinians or Arabs or Muslims when your argument boils down to ‘they are violent primitives and deserve to die,’ just going straight to dehumanization and ignoring all material conditions of Apartheid
Iraqi-born Israeli historian Avi Shlaim, speaking of the wave of Iraqi Jewish migration to Israel, concludes that, even though Iraqi Jews were “victims of the Israeli-Arab conflict”, Iraqi Jews aren’t refugees, saying “nobody expelled us from Iraq, nobody told us that we were unwanted.” He restated that case in a review of Martin Gilbert’s book, In Ishmael’s House.
Yehuda Shenhav has criticized the analogy between Jewish emigration from Arab countries and the Palestinian exodus. He also says “The unfounded, immoral analogy between Palestinian refugees and Mizrahi immigrants needlessly embroils members of these two groups in a dispute, degrades the dignity of many Mizrahi Jews, and harms prospects for genuine Jewish-Arab reconciliation.” He has stated that “the campaign’s proponents hope their efforts will prevent conferral of what is called a ‘right of return’ on Palestinians, and reduce the size of the compensation Israel is liable to be asked to pay in exchange for Palestinian property appropriated by the state guardian of ‘lost’ assets.”
Israeli historian Yehoshua Porath has rejected the comparison, arguing that while there is a superficial similarity, the ideological and historical significance of the two population movements are entirely different. Porath points out that the immigration of Jews from Arab countries to Israel, expelled or not, was the “fulfilment of a national dream”. He also argues that the achievement of this Zionist goal was only made possible through the endeavors of the Jewish Agency’s agents, teachers, and instructors working in various Arab countries since the 1930s. Porath contrasts this with the Palestinian Arabs’ flight of 1948 as completely different. He describes the outcome of the Palestinian’s flight as an “unwanted national calamity” that was accompanied by “unending personal tragedies”. The result was "the collapse of the Palestinian community, the fragmentation of a people, and the loss of a country that had in the past been mostly Arabic-speaking and Islamic.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jewish_exodus_from_the_Muslim_world







I added the link, those quotes show why most historians consider the comparison of the Nakba and Jewish exodus from the Muslim world to be a false equivalence. While there were certainly pogroms, the vast majority of Jewish immigrants were able to sell their possessions and willingly move. This is in contrast to the Nakba, where all 800,000 Palestinians were forcibly removed by a deliberate ethnic cleansing campaign. Whether you recognize it or not, when you bring up the exodus as a reaction to the Nakba with the conclusion that both sides are bad, the point of that argument is a justification for the Nakba.
If you’re Iraqi, how do you not see that all the different Arab countries have their own interests? While there was some semblance of pan-Islamism and pan-arabism during the British Mandate, it ultimately was a failed project. Jordan, Egypt, and other countries were not operating on the ‘behalf of Palestine,’ and their actions are not the fault of Palestinians.
You bring up the 1913 Pogroms and the 1930s Riots in Palestine in reaction to the Nakba too, as if they were fueled by Antisemitism instead of anti-settler-colonialism. Even the commissions done by the British disagree with that.
The Concept of forcible transfer the native Palestinians population was central to Zionism since the 1880s when Palestine was chosen as the location. During the British Mandate, around a 100,000 Palestinians were forcibly displaced by land purchases (unlike previous land purchases, where peasants would normally continue working and living on the land). Ben-Gurion used Partition as a tactic to dissuade the British from considering a Bi-National Secular State, and instead create a causi-belli for the beginning of a Jewish ethnostate within Palestine. The Nakba, or Plan Dalet, was deliberately planned for over a year. That ethnic cleansing campaign is directly responsible for the Palestinian Occupied Territories of East Jerusalem, the West Bank, and Gaza. The 1967 war was a deliberate tactic for Israel to take control of those areas and begin the never ending occupation, once those policies were practiced on the Palestinian population that remained in the Green Line after the Nakba.
So what are you trying to agrue? Because none of that is false.
The Concept of Transfer 1882-1948
Transfer Committee and the JNF led to Forced Displacement of 100,000 Palestinians throughout the mandate.
1967 war: Haaretz, Forward
Israel Martial Law and Defence (Emergency) Regulations practiced in the occupied territories after 1967